CAML Query tutorial for SharePoint
-
CAML - Collaborative Application Markup Language
-
XML- Extensible Markup Language based query language
CAML: Used to perform a query operation against SharePoint Lists
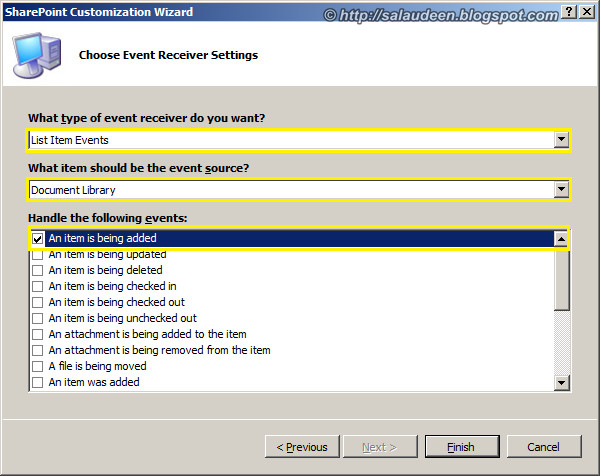
How SharePoint List Items are retrieved?
SharePoint List data can be retrieved in any one of the following ways:
1. Using the SharePoint object model – used when code runs on the server (Example: Developing a web part or an application page)
2. Using the SharePoint Lists web service – used when your code doesn’t run on the server where the SharePoint is installed (Example: Developing a windows application)
3. Using Power shell –used mostly by the ADMIN of the SharePoint when they quickly want to retrieve some information from the SharePoint site
How does CAML query looks like?
As I already mentioned, it is XML based query language and it contains tags in it. The root element of the CAML query root element is Query. But it is not necessary to use Query element in the query you form.
Within the Query element you have two elements possible:
1. Where – to filter the data
2. OrderBy – to categorize the data
A simple structure of the CAML query is as follows:
<Query>
<Where>
<Eq>
<FieldRef Name=”FieldName” />
<Value Type=”DataType”>Value</Value>
</Eq>
</Where>
<OrderBy>
<FieldRef Name=”FieldName” />
<FieldRef Name=”FieldName” />
</OrderBy>
</Query>
Operators in CAML Query
From the above structure, we came to know that it uses Where and OrderBy elements to retrieve the data from the list.
Let us know about the operators present in the CAML query and its usage:
Inside the Where element
1. Logical Operators - AND, OR
2. Comparison Operators - Listed Below in the table
AND – Which takes two conditions are satisfied
OR – Which takes when either of the conditions is satisfied
Comparison Operators
Inside the OrderBy/GroupBy element
OrderBy – Which orders or sort the data depends upon the field (FieldRef element) given.
GroupBy – Which groups the data depends upon the group by field (FieldRef element) given.
Examples
Logical & Comparison Operators
Use of AND, Gt, Leq
<Query>
<Where>
<And>
<Gt>
<FieldRef Name="Quantity" />
<Value Type="Number">0</Value>
</Gt>
<Leq>
<FieldRef Name="Price" />
<Value Type="Number">2000</Value>
</Leq>
</And>
</Where>
</Query>
Use of OR, Gt, Leq
<Query>
<Where>
<Or>
<Gt>
<FieldRef Name="Quantity" />
<Value Type="Number">0</Value>
</Gt>
<Leq>
<FieldRef Name="Price" />
<Value Type="Number">2000</Value>
</Leq>
</Or>
</Where>
</Query>
Use of BeginsWith, Leq
<Query>
<Where>
<And>
<BeginsWith>
<FieldRef Name="Title" />
<Value Type="Text">M</Value>
</BeginsWith>
<Leq>
<FieldRef Name="Quantity" />
<Value Type="Number">1000</Value>
</Leq>
</And>
</Where>
<OrderBy>
<FieldRef Name="Price" Ascending="False" />
</OrderBy>
</Query>
OrderBy Operator
<Query>
<Where>
<Or>
<Gt>
<FieldRef Name="Quantity" />
<Value Type="Number">0</Value>
</Gt>
<Leq>
<FieldRef Name="Price" />
<Value Type="Number">2000</Value>
</Leq>
</Or>
</Where>
<OrderBy>
<FieldRef Name="Price" Ascending="True" />
</OrderBy>
</Query>
CAML Query
-
A caml
query is build in two parts.
-
Sort
part is the sorting based on some columns
-
Filter part is the where clause of the CAML query
-
In order to
build up the XML for the CAML we create the where clause as follows:
-
Write the where clause just as you write in sql
-
Find
out the operators such as =, <=, <,> etc.
-
Find
out the keywords for these operators in CAML language. For example = is eq, < is
lt and so on.
-
Break the sql string such that the operator comes first and then comes the
operands. Continue this till the whole string is completed in this fashion.
-
Replace the operators with the keywords in CAML language.
-
Example: where column1=”a” and column2=”b” and column3 like ‘%c%’
-
=>
where (column1=”a” and column2=”b”) and column3 like ‘%c%’
-
=>
where and (column1=”a” and column2=”b”) (column3 like ‘%c%’)
-
=>
where and (and (column1=”a” column2=”b”) column3 like ‘%c%’)
-
=>
where and and (= column1 a column2 b) contains column3 c
-
=>
where and and eq column1 a eq column2 b contains column3 c
-
=>
<where>
<and>
<and>
<eq>
<FieldRef name=”Column1” />
<Value Type=string>a</Value>
</eq>
<eq>
<FieldRef name=”Column2” />
<Value Type=string>b</Value>
</eq>
</and>
<contains>
<FieldRef name=”Column3” />
<Value Type=string>c</Value>
</contains>
</and>
</where>